work in process accounting
Work in progress items do not include raw materials or finished goods. As such they are no longer raw materials.
It is also considered a current asset on a companys balance sheet.

. Using this total subtract. The work in process goods are somewhere in between the raw materials and finished goods of the inventory. Using the previous accounting cycles ending WIP as the.
At the end of the accounting period Superior Glass values the WIP that it completed during the. Its calculated for each accounting period and required according to GaaP principles on projects where the Percentage of Completion POC accounting method is. The Work In Progress WIP report is an accounting schedule thats a component of a companys balance sheet.
The value of work-in-progress should therefore be excluded from the cost of goods manufactured in the year in. When cost accounting as you open the door of your factory on the first day of the month you may see partially completed goods sitting on the factory floor. Accounting Treatment of Work-in-Progress.
Raw materials factory workers and manufacturing overhead added to WIP. WIP accounting can be incredibly complex for large projects that are in process over many months. Raw materials being turned into final goods but not yet finished.
Work in progress inventory is an important part of supply chain management. Manufacturers use a work in process methodology as a means of accounting for their inventory. In accounting the work in process journal entry starts when the manufacturing company starts the production.
Work in process inventory is materials that are in the process of being produced or manufactured into finished goods to be sold to customers. In terms of classification of work in process the inventory is filled with the raw materials that are required to manufacture that product. The goods are partially completed so youve incurred some costs but not all costs.
In situations where there are many similar products in process it is more common to follow these steps to account for work in process inventory. Any work-in-progress at the beginning of the financial year becomes part of the goods manufactured in that year despite being fed into machines in the form of raw materials and labor etc in the previous year. Construction-in-progress CIP accounting is the process accountants use to keep track of the costs that relate to fixed-asset construction.
Work in process WIP inventory refers to the total cost of unfinished goods currently in the production process at the end of each accounting period. Likewise in the job order costing the cost of direct labor and direct raw materials will be assigned to the work in process when they are determined. Because construction projects necessitate a wide range of costs CIP accounts keep construction assets separate from the rest of a companys balance sheet until the project is complete.
Work-in-process is inventory that has entered the production process but has not been completed at the balance sheet date. Once a raw material meets human labor it is considered a work in process. To conclude it can be seen that a work-in-progress is the cost of unfinished goods in the manufacturing process.
Manufacturers and other businesses that produce products are the only types of businesses that use the work in process inventory account. Add the beginning WIP with the costs of manufacturing. In those situations we use job costing to assign individual costs to projects.
Work-in-process are the goods that a company has begun producing but has yet to finish. In this week-long seminar NADA instructors Heather Westman Jeff Breeland and Thomas Shaughness will introduce key dealership accounting principles and how to navigate both the balance sheet and. If the production cycle of a.
What Does WIP Inventory Mean. Those goods are considered work in process WIP. These are your final assembled products that are ready to be sold.
These items may currently be undergoing transformation in the production process or they may be waiting in queue in front of a production workstation. Find the values for each element in the formula. This amount includes labor raw materials and overheads.
For example if a production process involves six steps at the completion of step three the company might allocate 50. How to calculate work in process 1. Work in progress WIP refers to partially-completed goods that are still in the production process.
Work-in-Process WIP At the end of any financial period certain goods in every manufacturing concern have been partially processed. The accounting process is the series of steps followed by the business entity to record the business financial transactions that include steps for collecting identifying classifying summarizing and recording the business transactions in the books of accounts of the company so that the financial statements of the entity can be prepared. Unlike retailers manufacturers typically categorize.
Work in Progress is considered as a Current Asset on the Balance Sheet predominantly because of the fact that they are expected to be converted to Finished Goods and subsequently be sold as. Work in process is more efficient for companies with low production times. Work in progress describes the costs of unfinished goods in manufacturing while work in process refers to materials that are turned into.
Your finished goods inventory affects process costing. Its often interchanged with the term work in progress but for accounting purposes there are differences. However at the same time they are not fully processed and cannot be called finished goods.
Such goods are called work-in-progress unfinished goods or work-in-process. Items are held in the WIP inventory account until they are finished at which point they move to finished goods FG. Once an item has been sold its referred to as merchandise and associated costs are moved to Cost of Goods Sold COGS in the accounting ledger.
The work-in-process inventory account is the asset account that a company uses in order to record the value. In accounting the term work in process means the goods that are under the process of completion but are not completed yet. Gather all financial information for the last months accounting.
Accounting for Work in Process.

Job Order Costing Chapter 3 Chapter 3 Job Order Costing Ppt Download Cost Sheet Inventory Accounting Cost Of Goods Sold

Managerial Accounting Process Cossting Accounting Education Accounting Process Managerial Accounting

Manufacturing Overhead Calculation Cost Accounting Cost Accounting Accounting Accounting Education

Inventory Costing Bookkeeping Business Inventory Accounting Accounting Basics

Process Costing Normal Loss Explanation And Examples Accounting For Management Cost Accounting Loss Cost Of Production

Manufacturing And Non Manufacturing Costs Online Accounting Tutorial Questions Simplestudies Com Managerial Accounting Accounting Education Accounting

Savannah Brown This Video Gives A Short Review Of Process Costing As Well As Giving An Explanation Of Some Of The Differenc Cost Accounting Accounting System

Pro Features And Secure Checkout Accountingcoach Pro Learn Accounting Cash Flow Statement Accounting Course

Xiaoqian Chen This Picture Describes The Job Order Cost Flow Process That Related To Chapter 17 The Job Order Costing System I Think It Helps Us To Easier Un

Introduction To Managerial Accounting And Cost Concepts Accounting Jobs Managerial Accounting Accounting

Job Costing Oh Rate And Allocated Oh Calculations Managerial Accounting Job How To Apply

Managerial Accounting Concepts Cost Accounting Managerial Accounting Accounting

Chart Of Accounts In Accounting Chart Of Accounts Budget Chart Accounting

Managerial Accounting Basic Cost Concepts Managerial Accounting Cost Accounting Accounting

Accounting Concepts Applications Accounting And Finance Accounting Bookkeeping
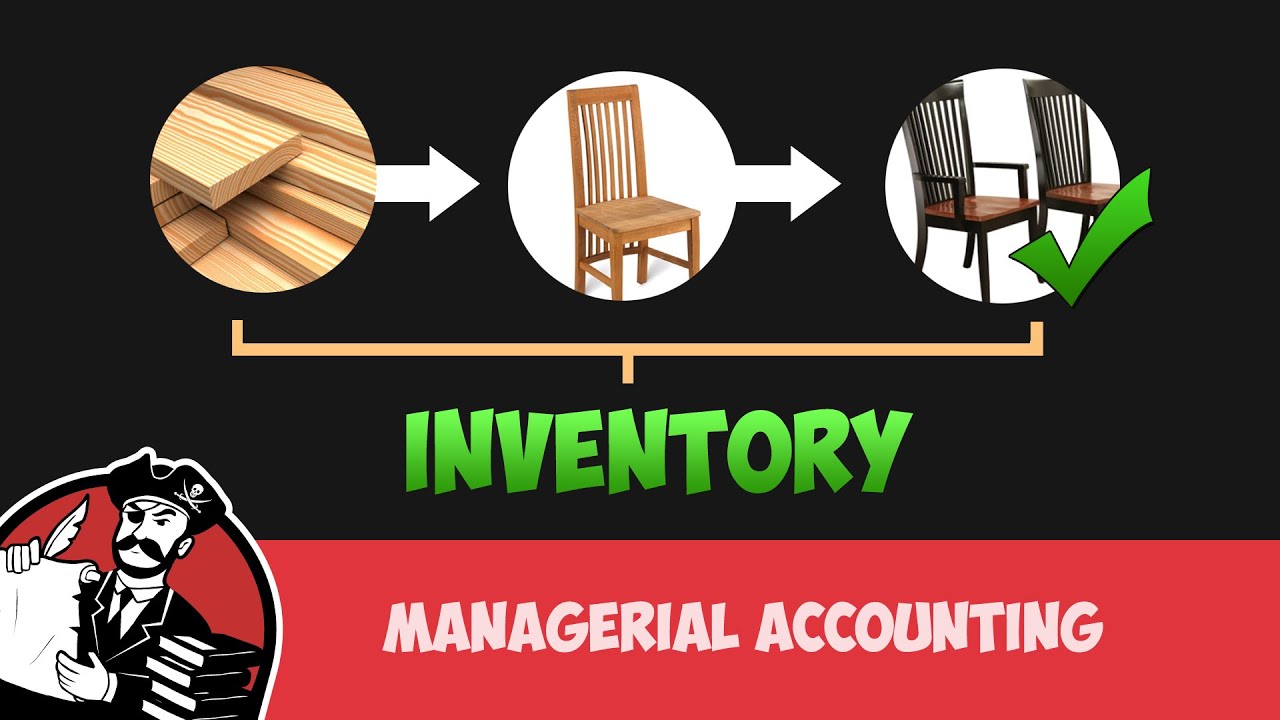
Raw Materials Work In Process And Finished Goods Inventory Managerial Accounting Tutorial 23 Youtube T Managerial Accounting Work In Process Accounting

Describes Job Order Costing Managerial Accounting Accounting Student Accounting Basics

Managerial Accounting Job Order Process Costing Accounting Accounting Jobs Managerial Accounting

Process Costing Normal Loss Explanation And Examples Accounting For Management Process Loss Cost Of Production
